"Meta AI decodes internal speech with 80% accuracy using non-invasive brain activity analysis, a groundbreaking breakthrough."
In the realm of cognitive science and artificial intelligence, groundbreaking breakthroughs are rare. Yet, Meta AI's recent achievement in decoding internal speech using non-invasive brain activity analysis is nothing short of revolutionary.
These diagrams show where scientists implanted small microelectrode arrays into the brains of two participants. These arrays collect signals which can be used to decode the internal monologue
Unveiling the Technology
Meta AI has pioneered a cutting-edge method that pushes the boundaries of what we thought possible. Their technology boasts an impressive 80% accuracy in decoding internal speech, a feat previously unimaginable.
The Non-Invasive Approach
Unlike invasive methods that require implants or electrodes, Meta AI's approach is entirely non-invasive. By analyzing brain activity through non-intrusive means, such as EEG or functional MRI, they can decipher the intricate patterns associated with internal speech.
Unraveling the Complexity of Speech
Speech, both internal and external, is a complex interplay of neural signals and cognitive processes. Meta AI's technology delves deep into this complexity, extracting meaningful information from the neural patterns that underlie our thoughts and speech.
The participants were initially instructed to think of the word—for example, "spoon," "python," or "battlefield"—internally after hearing or seeing a spoken or visual trigger.
The researchers achieved up to 79% accuracy in decoding the internally spoken phrases in real time.
This was accomplished by electrodes affixed to the supramarginal gyrus, a region of the brain crucial to the comprehension of spoken and written language.
The apparatus demonstrated the ability to decipher various internal speaking methods, such as silent reading of the word and visualization of the item it represents.
The technology functions on the same premise as other brain-machine interface devices, like Neuralink, which is developed by Elon Musk.
Unlike this gadget, Neuralink converts the electrical information it gets from the brain into a set of movement commands so it can communicate with machines.
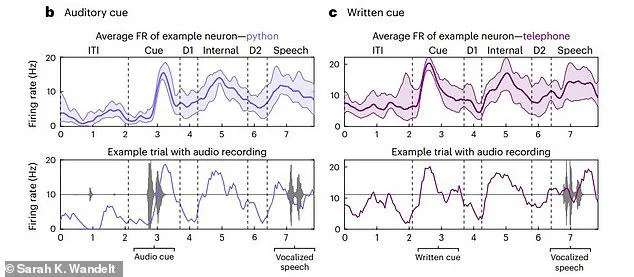
This diagram shows how accurately the scientists were able to decode eight words. The boxes on the far right show how participant one's internal monologue (top) could be decoded with up to 91 per cent accuracy for some words while participant two (bottom) proved harder to decoden the trials, participants were cued a word and asked to vocalise it or say it internally. The graphs show the activity of a single neuron in their brain while saying 'python' or 'telephone'. In the bottom graphs you can see in black the sound waves of the cue and speech
The Implications for Communication
The implications of Meta AI's breakthrough are profound. Imagine a world where individuals with speech impairments can communicate effortlessly using their thoughts alone. Or where silent conversations can unfold between individuals, facilitated by technology that understands the unspoken word.
Beyond Communication: Medical Applications
Beyond its applications in communication, Meta AI's technology holds promise in the field of medicine. It opens doors to better understanding neurological disorders, such as aphasia or schizophrenia, by providing insights into the underlying neural mechanisms.
Meta AI creates a non-invasive technique to interpret brain activity in voice
Ethical Considerations and Privacy Concerns
However, with such advancements come ethical considerations and privacy concerns. The ability to decode internal speech raises questions about consent, privacy, and the potential for misuse. It is imperative that Meta AI and other stakeholders navigate these issues with care and responsibility.
Looking Ahead
As we stand on the cusp of a new era in cognitive technology, the possibilities seem limitless. Meta AI's groundbreaking breakthrough in decoding internal speech is just the beginning. With further research and development, we can expect even more astounding advancements in the years to come.

















0 Comments